Welcome to a weekly series where I break down and compare some of the most popular exchange-traded funds (ETFs) available to Canadian investors!
Canadian investors favouring the most hands-off, passive approach to investing can eschew a hand-picked portfolio of stocks and bonds for an all-in-one asset-allocation ETF. Both Vanguard and BlackRock provide a set of tickers for these ETFs.
Today, we’ll be looking at the 80/20 stocks/bonds version, otherwise known as the “growth” ETF portfolio, suitable for investors with a medium-risk tolerance. Up for consideration are Vanguard Growth ETF Portfolio (TSX:VGRO) and iShares Core Growth ETF Portfolio (TSX:XGRO).
VGRO vs. XGRO: Fees
The fee charged by an ETF is expressed as the management expense ratio (MER). This is the percentage that is deducted from the ETF’s net asset value (NAV) over time and calculated on an annual basis. For example, an MER of 0.50% means that for every $10,000 invested, the ETF charges a fee of $50 annually.
VGRO has an MER of 0.24% compared to XGRO at 0.20%. The difference is miniscule (a difference of $4 on a $10,000 portfolio), but if we had to pick a winner, it would be XGRO.
VGRO vs. XGRO: Size
The size of an ETF is very important. Funds with small assets under management (AUM) may have poor liquidity, low trading volume, high bid-ask spreads, and more risk of being delisted due to lack of interest.
VGRO currently has AUM of $3.44 billion, whereas XGRO has AUM of $1.37 billion. Although both are sufficient for a buy-and-hold investor, VGRO is clearly the more popular one.
VGRO vs. XGRO: Holdings
Both ETFs here are considered “funds of funds” in that their underlying holdings are not stocks but rather other ETFs. This makes sense, as XGRO and VGRO are intended to be all-in-one portfolios.
XGRO chooses to allocate approximately 36% to the U.S. stock market, 21% to the Canadian stock market, 19% to the developed international stock market, 4% to the emerging international stock market, 16% to the Canadian bond market, and 4% to the U.S. bond market.
VGRO chooses to allocate approximately 34% to the U.S. stock market, 25% to the Canadian stock market, 15% to the developed international stock market, 6% to the emerging international stock market, 12% to the Canadian bond market, 4% to the U.S. bond market, and 4% to the global ex-U.S. bond market.
VGRO vs. XGRO: Historical performance
Both funds are quite new, so their performance history is rather limited. Nonetheless, a backtest is useful for assessing their tracking error and relative performance.
A cautionary statement before we dive in: past performance is no guarantee of future results, which can and will vary. The portfolio returns presented below are hypothetical and backtested. The returns do not reflect trading costs, transaction fees, or taxes, which can cause drag.
Here are the trailing returns from 2019 to present:
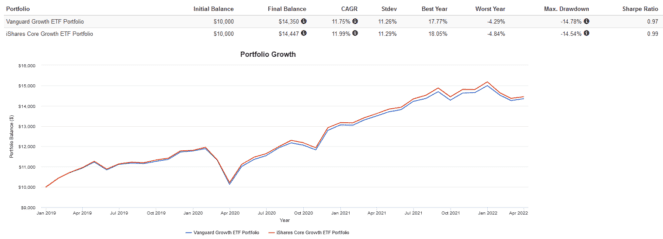
Here are the annual returns from 2019 to present:
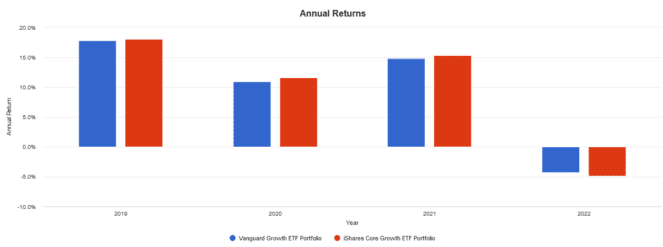
Both ETFs have very similar performance. XGRO had slightly higher returns and volatility due to its higher concentration of U.S. stocks. Over the long run, I expect their performance to be virtually identical.
The Foolish takeaway
If I had to choose one ETF to buy and hold, it would be VGRO. Despite the 0.04% higher MER, the higher AUM of the fund and its larger proportion of Canadian stocks appeal to me due to lower currency volatility. Both funds have roughly the same holdings with good diversification. Still, if you’re partial to BlackRock, XGRO is a fantastic choice as well.








