Most investors (including me) will find it very difficult to beat the market consistently. While some investors can get lucky and outperform it in the short term, many will fail to over the long run. Even fund managers and stock pickers often underperform a simple index fund over time. The market is efficient, and the various stock market indexes out there are notoriously difficult to beat.
The S&P 500 Index
The most famous index, and the benchmark many professional investors measure themselves against is the S&P 500. The S&P 500 tracks the largest 500 companies listed on U.S. exchanges and is widely seen as a barometre for overall U.S. stock market performance. It makes for a great passive investment.
If you are comfortable with using Norbert’s Gambit to convert CAD to USD for cheap (which I covered earlier with a how-to guide) and are investing in your Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP), you can save significantly by using a U.S.-denominated S&P 500 exchange-traded fund (ETF) like Vanguard S&P 500 Index ETF (NYSE:VOO).
VOO is as cheap as it gets for ETFs, costing just 0.03% per year in management expense ratios (MER). That’s around $3 per year for a $10,000 investment, making VOO a perfect low-cost vehicle for tracking a well-known, high-performing index.
The total U.S. stock market
That being said, the U.S. stock market doesn’t end at just the S&P 500. Beyond the index, there are another +3,000 mid-, small-, and micro-cap stocks out there worth investing in. These stocks often have different risk/reward profiles, and their volatility can help boost long-term returns.
By market capitalization, the S&P 500 accounts for around 82% of the U.S. stock market’s weight. That means there’s another 18% of stocks out there unaccounted for. To track these stocks, investors can turn to the CRSP U.S. Total Market Index.
To track this index, consider buying Vanguard Total Stock Market Index ETF (NYSE:VTI). Compared to VOO, VTI holds over 3,000 more mid-, small-, and micro-cap stocks. Roughly 82% of VTI is VOO, making their performance and composition somewhat similar. Surprisingly, VTI is just as inexpensive as VOO is, costing just 0.03% in MER.
Head to head
Over very long periods of time, VTI can be expected to perform very similarly to VOO, but with higher volatility. Because 82% of VTI is VOO, its performance is still highly correlated to the S&P 500. The remaining 12% of mid- and small-cap stocks adds some volatility, which can boost returns but also increases risk.
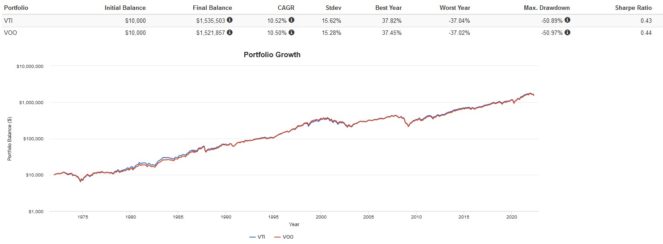
I’ve backtested the returns of the S&P 500 vs. the total U.S. stock market from 1972 below. A cautionary statement before we dive in: past performance is no guarantee of future results, which can and will vary. The portfolio returns presented below are hypothetical and backtested. The returns do not reflect trading costs, transaction fees, or taxes.
Trailing returns are virtually identical, with VTI having slightly more volatility but also higher returns.
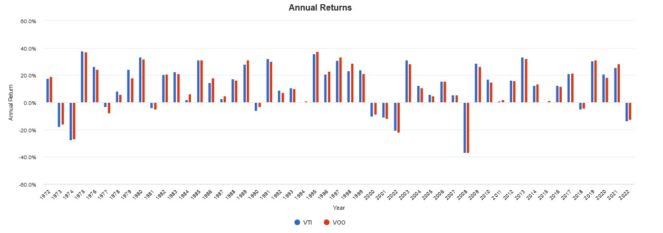
Annual returns are similar too, with VTI outperforming some years, and VOO in others. I attribute this to the cyclical nature of small- and large-cap stocks, which take turns outperforming.
The Foolish takeaway
My pick here is VTI. We don’t know whether small or large caps will do better in the future. The evidence suggests that both are cyclical. Large caps did particularly well in the last decade, but small caps outperformed in the years following the dot-com bubble. While the S&P 500 is a solid investment, investors seeking a truly passive approach should buy the total U.S. stock market. This is all the more compelling when you consider that VOO and VTI cost the same MER.
 Claim Membership Credit
Claim Membership Credit







